New Milford’s first library was established in 1796. Housed in the homes of five different “public spirited citizens” it was ironically known as the Union Library. The library was open only five days a year, and consisted of 350 books. A century later, the New Milford Library Association was founded and the collection was relocated to the town hall.
New Milford’s first library was established in 1796. Housed in the homes of five different “public spirited citizens” it was ironically known as the Union Library. The library was open only five days a year, and consisted of 350 books. A century later, the New Milford Library Association was founded and the collection was relocated to the town hall.
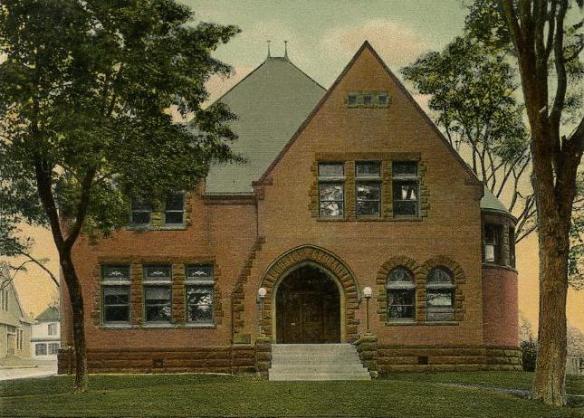
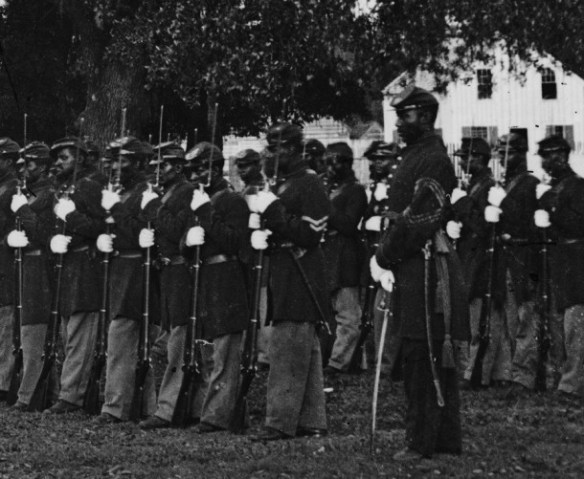
In 1893, the General Assembly of Connecticut passed a bill “authorizing the Town of New Milford to erect a library building and memorial hall,” honoring the 267 soldiers and sailors from New Milford who served in the Civil War. The legislation further specified that the structure was “also to contain the tablets, emblems, and inscriptions commemorative of those soldiers who enlisted from said New Milford, and for meetings of the Grand Army and for other literary, patriotic, and historical purposes such as the town may prescribe.”
The “Grand Army” was the Grand Army of the Republic, a fraternal organization comprised of veterans of the Union Army. Founded in Decatur, Illinois in 1866, the GAR became among the first – and arguably one of the most successful – lobbying organizations. At its peak it consisted of 490,000 Civil War veterans. The GAR supported voting rights for African American veterans, furthered the careers of Republican politicians, and pushed for Congress to establish veterans pensions. (The GAR was so successful in this last endeavor that as of 2013, one pension is still being paid – $876 a year to the daughter of a Civil War veteran born around 1930!)
Egbert Marsh, a prominent citizen, offered the town a lot on Main Street and $10,000 toward the construction of a new building, with individuals contributing the balance. Marsh donated additional money to purchase books for the collection. The library building was erected in 1897. The reading room opened in January 1898, and the circulation of books began two months later. The second story of the building served sat the headquarters of the GAR’s Upton Post, which was organized in 1882 with 26 charter members.
Egbert Marsh died in 1896 and never saw the completed structure. The second story of the library, devoted to public lectures and meetings, is still called Memorial Hall, however, and its walls are decorated with prominent images and documents from the Civil War.